Simple Eating Habits for Better Long-Term Health: 16 Smart Practices That Truly Last
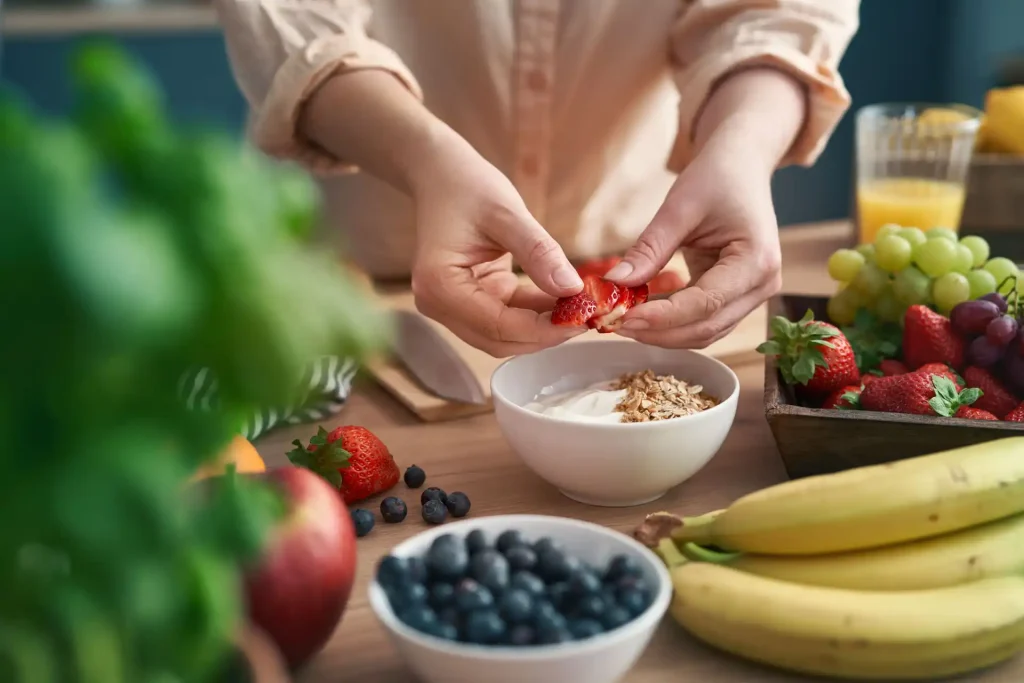

Healthy eating doesn’t have to be complicated, restrictive, or stressful. In fact, the most effective changes are often the simplest ones—small habits practiced consistently over time. Adopting Simple Eating Habits for Better Long-Term Health can significantly improve energy levels, digestion, immune strength, and overall quality of life.
Many people struggle with nutrition because they believe healthy eating requires strict diets or constant self-control. The truth is that long-term health comes from realistic, repeatable habits that fit into everyday life. According to the World Health Organization, sustainable eating patterns rich in whole foods and balanced nutrients are key to preventing chronic diseases and supporting lifelong well-being.
This in-depth guide explores practical eating habits that are easy to follow, scientifically sound, and designed to benefit your health for years—not just weeks.
Why Eating Habits Matter More Than Diets
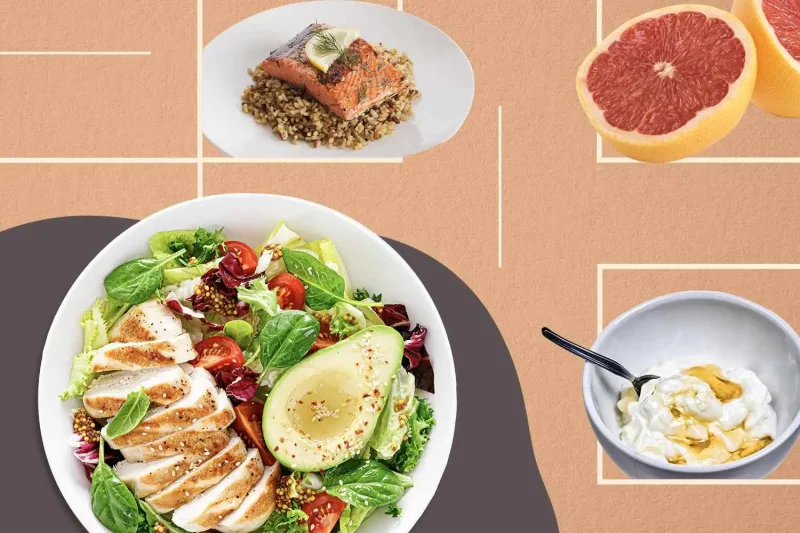

Diets are temporary, but habits shape your health for a lifetime. Strict diets often lead to short-term results followed by burnout, weight regain, and frustration. Eating habits, on the other hand, influence how you eat day after day—without pressure or guilt.
Simple Eating Habits for Better Long-Term Health focus on consistency rather than perfection. When healthy choices become routine, they no longer feel like effort. This approach supports steady energy, balanced weight, and better metabolic health over time.
Focus on Whole, Minimally Processed Foods
Whole foods are foods that are close to their natural form and rich in nutrients.
Examples include:
-
Fruits and vegetables
-
Whole grains
-
Lean proteins
-
Nuts, seeds, and legumes
These foods provide fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that protect against inflammation, heart disease, and metabolic disorders. Choosing whole foods most of the time is one of the most powerful eating habits you can develop.
Eat Regular, Balanced Meals

Skipping meals or eating erratically disrupts blood sugar levels and increases cravings.
Balanced meals typically include:
-
A source of protein
-
Complex carbohydrates
-
Healthy fats
-
Fiber-rich vegetables or fruits
Eating regularly supports digestion, energy stability, and hormonal balance—key pillars of long-term health.
Practice Mindful Eating
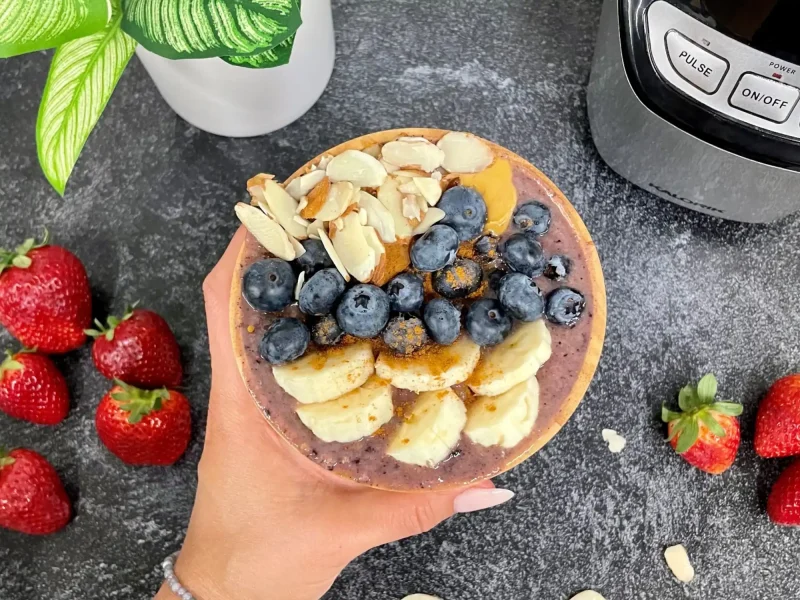

Mindful eating means paying attention to what and how you eat.
Simple mindful habits include:
-
Eating slowly
-
Chewing thoroughly
-
Avoiding screens during meals
-
Listening to hunger and fullness cues
Mindful eating improves digestion, reduces overeating, and helps build a healthier relationship with food.
Prioritize Protein at Every Meal

Protein supports muscle health, metabolism, immune function, and satiety.
Good protein sources include:
-
Eggs
-
Fish and poultry
-
Beans and lentils
-
Dairy or fortified alternatives
-
Nuts and seeds
Including protein in each meal helps control appetite and preserves muscle mass as you age.
Include Fruits and Vegetables Daily
Fruits and vegetables provide essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and disease-fighting compounds.
Aim to:
-
Include vegetables at most meals
-
Eat a variety of colors
-
Choose seasonal or frozen options
Regular fruit and vegetable intake reduces the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Choose Healthy Fats Consistently

Healthy fats support brain health, hormone production, and nutrient absorption.
Sources of healthy fats include:
-
Olive oil
-
Avocados
-
Fatty fish
-
Nuts and seeds
Replacing processed fats with healthier options is a simple habit with long-lasting benefits.
Stay Properly Hydrated
Water supports digestion, circulation, temperature regulation, and detoxification.
Helpful hydration habits:
-
Drink water throughout the day
-
Start your morning with water
-
Limit sugary drinks
Even mild dehydration can affect energy and concentration, making hydration a key part of long-term health.
Control Portions Without Restriction
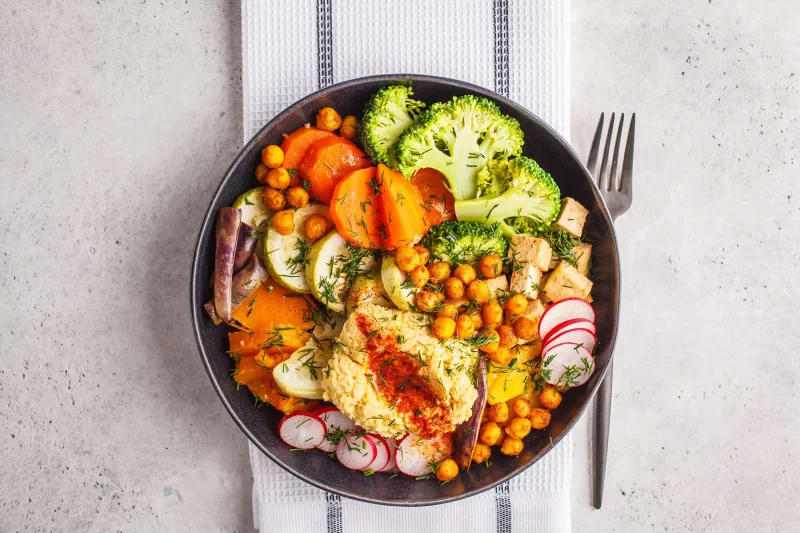
Portion control doesn’t require measuring or calorie counting.
Practical strategies include:
-
Using smaller plates
-
Eating until comfortably full
-
Slowing down during meals
This habit prevents overeating while still allowing enjoyment of food.
Limit Added Sugar and Ultra-Processed Foods
Ultra-processed foods are often high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats but low in nutrients.
Reducing them helps:
-
Stabilize energy levels
-
Improve gut health
-
Lower inflammation
You don’t need to eliminate them completely—just limit them and prioritize nutrient-dense foods.
Cook More Meals at Home
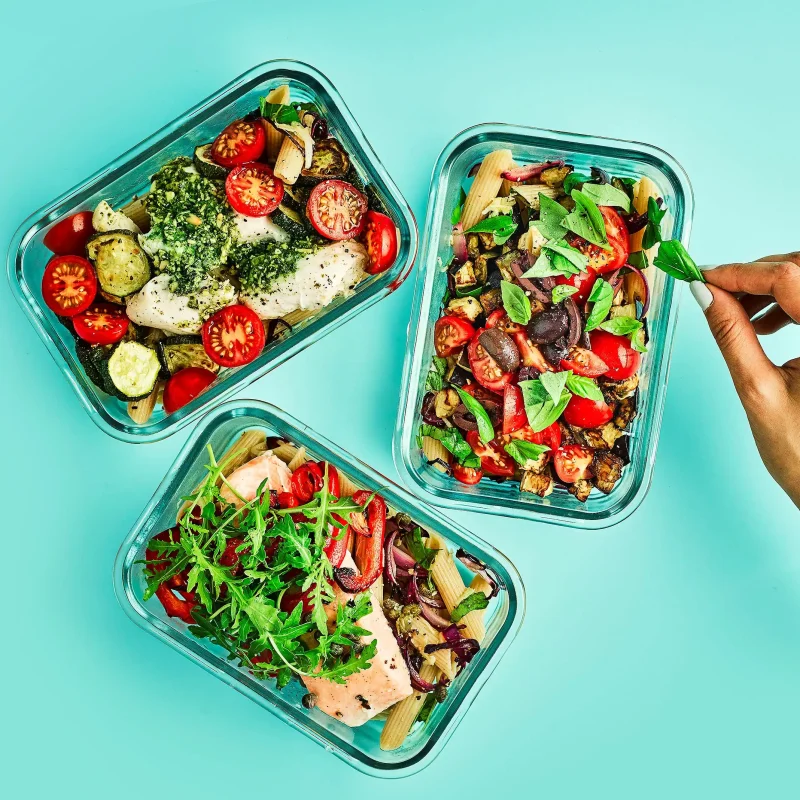

Cooking at home gives you control over ingredients and portion sizes.
Benefits include:
-
Better nutrient quality
-
Reduced added sugars and fats
-
Improved eating awareness
Even simple home-cooked meals support better long-term health than frequent takeout.
Build a Healthy Relationship With Food
Healthy eating should not involve guilt or fear.
Positive habits include:
-
Allowing flexibility
-
Enjoying favorite foods mindfully
-
Avoiding labeling foods as “good” or “bad”
A balanced mindset promotes emotional well-being and sustainable habits.
Simple Eating Habits for Busy Lifestyles
Even with limited time, healthy habits are possible.
Try:
-
Planning meals ahead
-
Keeping healthy snacks available
-
Using frozen or pre-cut vegetables
-
Eating simple, repeatable meals
Consistency matters more than complexity.
Long-Term Benefits of Healthy Eating Habits
Over time, Simple Eating Habits for Better Long-Term Health can lead to:
-
Stable energy levels
-
Stronger immunity
-
Better digestion
-
Healthy weight maintenance
-
Reduced risk of chronic disease
-
Improved mental clarity and mood
These benefits compound gradually, making small habits incredibly powerful.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long does it take to see benefits from better eating habits?
Many people notice improvements in energy and digestion within a few weeks.
2. Do I need to follow a specific diet plan?
No. Simple, balanced habits are more effective than rigid diet plans.
3. Can I still enjoy treats?
Yes. Long-term health allows flexibility and enjoyment in moderation.
4. Are eating habits more important than exercise?
Both matter, but eating habits have a larger daily impact on overall health.
5. Is healthy eating difficult to maintain long term?
Not when habits are simple, realistic, and aligned with your lifestyle.
6. Can these habits work at any age?
Yes. Simple eating habits benefit children, adults, and older individuals alike.
Conclusion
Adopting Simple Eating Habits for Better Long-Term Health is one of the most effective ways to protect your body, mind, and future well-being. You don’t need perfection or extreme rules—just consistent, thoughtful choices made most of the time.
By focusing on whole foods, balanced meals, mindful eating, and flexibility, you create a lifestyle that supports health for years to come. Start small, stay consistent, and let your habits work for you.







