Esomeprazole For Dogs: Uses, Dosage, & Side Effects
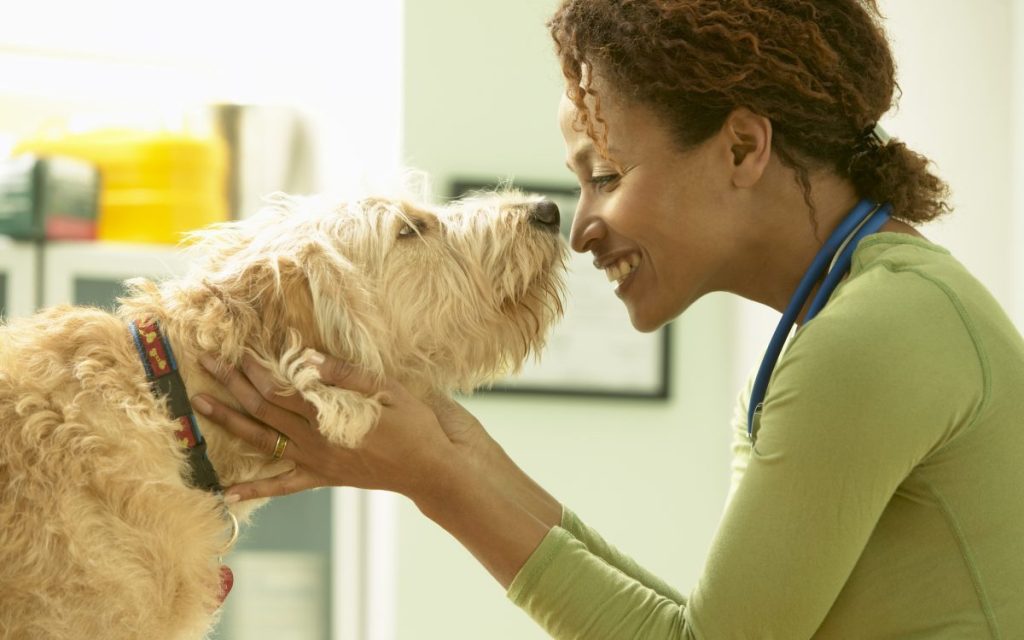

Esomeprazole for dogs is a proton pump inhibitor medicine that veterinarians usually prescribe to treat heartburn, or acid reflux, along with stomach and intestinal ulcers. It’s the generic name for a medicine that is also sold under the brand name Nexium. Here’s what you should know about the uses, dosage, and side effects of esomeprazole for dogs.
Uses of esomeprazole for dogs
Veterinarians generally recommend esomeprazole for dogs to treat heartburn or acid reflux. This lowers the pH level of the stomach, which in turn helps it to heal. The drug can also treat stomach and intestinal ulcers. The drug works by preventing the stomach from producing too much gastric acid.
Although the FDA hasn’t approved this medication for use with dogs, vets can safely prescribe it. You must closely follow your vet’s instructions for the correct and safe dosage and frequency.
Esomeprazole is available as a tablet or oral suspension. While low-dose versions may be available without a veterinarian’s prescription, you should never administer this medication to your dog without first consulting your vet.
Dosage of esomeprazole for dogs
While online guidelines provide general information on the drug’s use in dogs, they should never replace your veterinarian’s advice for your dog.
Your veterinarian will prescribe esomeprazole in a dosage that reflects the severity of your dog’s condition. If they prescribe the tablet form, veterinarians usually recommend a dosage that will be determined based on your dog’s weight.
If your vet prescribes the drug as an oral suspension, then they’ll show you how to use it safely on your dog, along with detailing the precise dosage.
It’s important to always follow your vet’s dosage and administration instructions exactly. This includes the length of time the medicine you should give the medicine to your dog.
Side effects of esomeprazole for dogs
Side effects of esomeprazole in dogs are said to be uncommon, but in some cases, the animal might suffer from diarrhea, vomiting, or urinary tract infections.
Veterinarians usually recommend that dogs with liver conditions do not take this drug.
If you see signs of a serious allergic reaction in your dog, including swelling, hives, difficulty breathing, or other symptoms, then you must contact your veterinarian immediately.
If you suspect your dog took too much of the medication and is suffering from an overdose, contact an emergency veterinarian right away.