How Food Choices Influence Gut Health and Digestion: 15 Science-Backed Insights for a Healthier Gut

Your digestive system does far more than break down food—it plays a central role in immunity, energy production, nutrient absorption, and even mental health. What you eat daily directly shapes how well your gut functions. Understanding How Food Choices Influence Gut Health and Digestion empowers you to improve digestion naturally and support long-term wellness from the inside out.
Modern diets high in ultra-processed foods, sugar, and low fiber have contributed to widespread digestive issues such as bloating, constipation, acid reflux, and gut inflammation. According to the World Health Organization, diets rich in whole foods and dietary fiber are essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system and preventing chronic disease.
This comprehensive guide explains how specific food choices affect gut health, the gut microbiome, and digestion—and how simple changes can lead to noticeable improvements.
Understanding the Gut and Digestive System
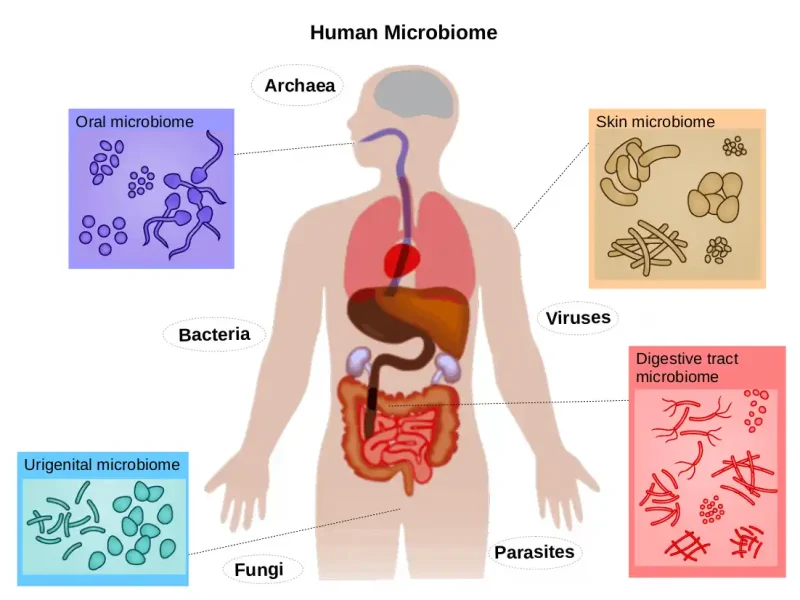
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. It includes the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and trillions of microorganisms living in the gut.
What Is Gut Health?
Gut health refers to how efficiently the digestive system functions and how balanced the gut microbiome is. A healthy gut supports:
-
Smooth digestion
-
Strong immunity
-
Reduced inflammation
-
Stable energy and mood
This is why understanding How Food Choices Influence Gut Health and Digestion is so important for overall wellness.

The Gut Microbiome Explained
The gut microbiome is made up of trillions of bacteria, fungi, and microorganisms living in the intestines.
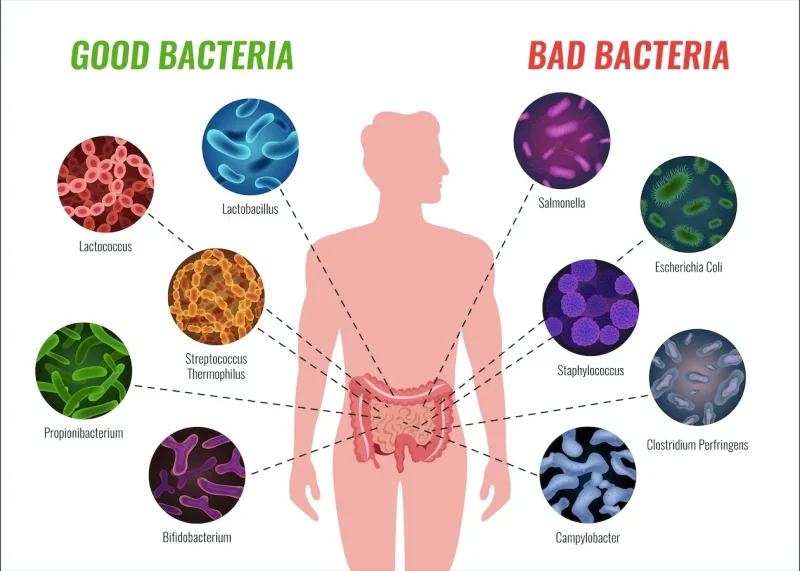
Good vs. Harmful Gut Bacteria
Beneficial bacteria help:
-
Digest fiber
-
Produce vitamins
-
Protect against harmful pathogens
-
Reduce inflammation
Poor food choices can reduce beneficial bacteria and allow harmful microbes to thrive, leading to digestive discomfort and poor health outcomes.
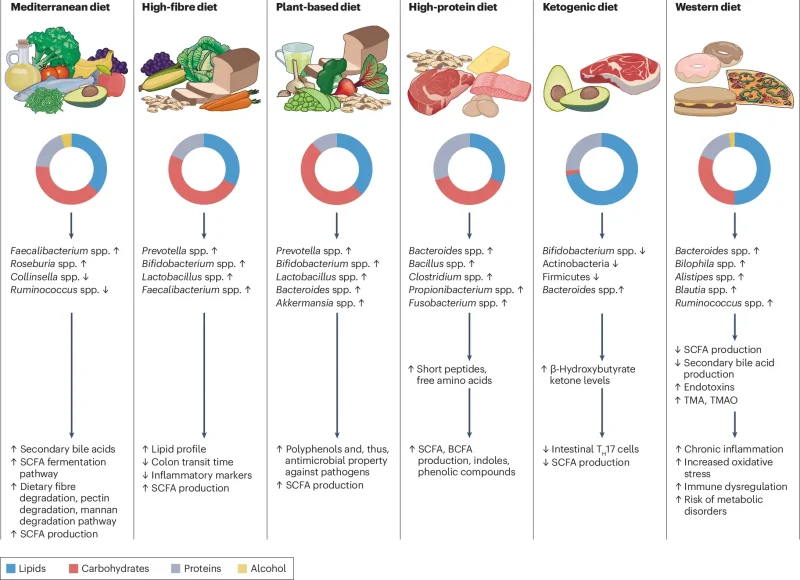
How Food Choices Shape Gut Health
Fiber and Digestive Function
Dietary fiber is one of the most important nutrients for gut health.
Fiber:
-
Feeds beneficial gut bacteria
-
Supports regular bowel movements
-
Prevents constipation
-
Reduces gut inflammation
Low-fiber diets slow digestion and weaken the gut microbiome, clearly demonstrating How Food Choices Influence Gut Health and Digestion.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
-
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods.
-
Prebiotics are fibers that feed those bacteria.
Together, they help maintain microbial balance, improve digestion, and strengthen immunity.
Healthy Fats and Digestion
Healthy fats support bile production, which helps digest fat-soluble vitamins.
Sources include:
-
Olive oil
-
Avocados
-
Nuts and seeds
-
Fatty fish
Balanced fat intake supports smoother digestion and gut lining health.
Foods That Support Gut Health
Fruits, Vegetables, and Whole Grains
These foods provide fiber, antioxidants, and plant compounds that support microbial diversity.
Examples include:
-
Berries
-
Leafy greens
-
Oats
-
Brown rice
-
Legumes
Greater diversity in plant foods leads to a healthier gut microbiome.
Fermented Foods
Fermented foods naturally contain probiotics.
Examples:
-
Yogurt
-
Kefir
-
Sauerkraut
-
Kimchi
-
Miso
Regular consumption improves digestion and strengthens gut bacteria balance.
Foods That Harm Gut Health
Ultra-Processed Foods
Highly processed foods often lack fiber and contain additives that disrupt gut bacteria.
They are linked to:
-
Bloating
-
Irregular digestion
-
Increased gut inflammation
Excess Sugar and Artificial Additives
High sugar intake feeds harmful bacteria and yeast, leading to imbalance. Artificial sweeteners may also negatively affect gut bacteria composition in some individuals.
Gut Health, Immunity, and Inflammation
Over 70% of the immune system resides in the gut. A healthy diet strengthens the gut barrier, reducing inflammation and preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream.
This highlights How Food Choices Influence Gut Health and Digestion far beyond digestion alone.
Common Digestive Problems Linked to Diet

Poor food choices contribute to:
-
Constipation
-
Diarrhea
-
Bloating and gas
-
Acid reflux
-
Irritable bowel symptoms
Improving diet quality often reduces these symptoms without medication.
Simple Eating Habits for Better Digestion
Helpful habits include:
-
Eating slowly and chewing well
-
Staying hydrated
-
Eating regular meals
-
Reducing late-night eating
-
Managing stress
These habits support digestion alongside healthy food choices.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long does it take to improve gut health through diet?
Many people notice improvements in digestion within 2–4 weeks.
2. Is fiber more important than probiotics?
Both are important. Fiber feeds gut bacteria, while probiotics add beneficial strains.
3. Can gut health affect mental health?
Yes. The gut-brain connection links digestion with mood and cognition.
4. Are digestive supplements necessary?
Most people can improve gut health through food alone.
5. Does drinking water help digestion?
Yes. Hydration supports stool movement and nutrient absorption.
6. Can children benefit from gut-healthy diets?
Absolutely. Gut health is important at all ages.
Conclusion
Understanding How Food Choices Influence Gut Health and Digestion reveals how powerful everyday eating habits truly are. The foods you choose can either nourish your gut microbiome or disrupt it—affecting digestion, immunity, energy, and overall health.
By prioritizing fiber-rich foods, fermented options, hydration, and mindful eating, you support a resilient digestive system that benefits your entire body. Small, consistent changes can lead to lasting gut health and improved well-being.







