Balanced Nutrition Basics for Everyday Health: 15 Essential Principles You Should Follow

Good nutrition is the foundation of a healthy, energetic, and balanced life. What you eat every day directly influences your energy levels, immune strength, mental clarity, and long-term health. Understanding Balanced Nutrition Basics for Everyday Health helps you make smarter food choices without confusion, restriction, or stress.
In a world filled with fad diets and conflicting nutrition advice, balanced nutrition offers a simple, sustainable approach. It focuses on nourishing your body with the right mix of nutrients rather than eliminating entire food groups. According to the World Health Organization, a balanced diet is essential for preventing chronic disease, maintaining a healthy weight, and supporting overall well-being at every stage of life.
This comprehensive guide breaks down balanced nutrition into easy-to-understand concepts you can apply immediately—no special products or extreme rules required.
What Is Balanced Nutrition?

Balanced nutrition means consuming a variety of foods in the right proportions to provide the body with essential nutrients. It does not involve strict dieting or eliminating foods but focuses on balance, moderation, and consistency.
Why Balanced Nutrition Matters
Your body relies on nutrients for every function—breathing, thinking, moving, and healing. When nutrition is unbalanced, deficiencies or excesses can develop, leading to fatigue, weakened immunity, poor concentration, and increased disease risk. Understanding Balanced Nutrition Basics for Everyday Health empowers you to support your body proactively rather than reacting to health problems later.
Understanding Macronutrients

Macronutrients are nutrients the body needs in larger amounts to function properly. They include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Carbohydrates: Your Body’s Main Energy Source
Carbohydrates are the primary fuel for the brain and muscles. They should not be feared or avoided.
Healthy carbohydrate sources include:
-
Whole grains
-
Fruits
-
Vegetables
-
Legumes
Choosing complex carbohydrates over refined ones provides steady energy and supports digestion.
Proteins: Building and Repairing the Body

Protein is essential for muscle repair, immune function, and hormone production.
Good protein sources include:
-
Lean meats and poultry
-
Fish and eggs
-
Beans and lentils
-
Nuts, seeds, and dairy
Including protein in every meal helps maintain muscle mass and promotes satiety.
Fats: Essential for Hormones and Brain Health
Dietary fats support brain function, hormone production, and nutrient absorption.
Healthy fats include:
-
Olive oil
-
Avocados
-
Nuts and seeds
-
Fatty fish
Balanced nutrition focuses on healthy fats while limiting trans and highly processed fats.
Micronutrients and Their Role in Health

Micronutrients are vitamins and minerals needed in smaller amounts but are vital for daily function.
Vitamins for Daily Function
Vitamins support immunity, energy metabolism, vision, and skin health. A varied diet rich in fruits and vegetables ensures adequate vitamin intake without supplements in most cases.
Minerals That Support the Body
Minerals such as calcium, iron, magnesium, and potassium play roles in bone strength, oxygen transport, muscle contraction, and nerve signaling. Whole foods provide these minerals in bioavailable forms.
Building a Balanced Plate

One of the simplest ways to apply Balanced Nutrition Basics for Everyday Health is by visualizing your plate.
A balanced plate generally includes:
-
Half vegetables and fruits
-
One-quarter protein
-
One-quarter whole grains
-
A small portion of healthy fats
This method simplifies portion control and ensures nutrient diversity.
Portion Control Made Simple
Balanced nutrition is not only about what you eat but also how much you eat. Paying attention to hunger and fullness cues helps prevent overeating without strict calorie counting.
Hydration and Everyday Health
Water is essential for digestion, circulation, temperature regulation, and detoxification. Mild dehydration can cause fatigue, headaches, and poor concentration.
Hydration tips include:
-
Drinking water consistently throughout the day
-
Increasing intake during physical activity
-
Limiting sugary beverages
Proper hydration complements balanced nutrition and supports overall health.
Balanced Nutrition for Different Lifestyles

Nutrition for Busy Schedules
Balanced nutrition is achievable even with limited time.
Simple strategies include:
-
Preparing meals in advance
-
Choosing whole-food snacks
-
Keeping healthy staples on hand
-
Reading food labels carefully
Consistency matters more than perfection.
Nutrition Across Age Groups
Nutritional needs change with age. Children need nutrients for growth, adults for maintenance and energy, and older adults for bone health and muscle preservation. Balanced nutrition adapts to these needs without drastic changes.
Common Nutrition Myths
Many misconceptions make healthy eating confusing.
Common myths include:
-
Carbohydrates are bad
-
Fat causes weight gain
-
Supplements can replace food
-
Skipping meals improves health
Understanding Balanced Nutrition Basics for Everyday Health helps separate fact from fiction and promotes informed choices.
Simple Tips for Long-Term Healthy Eating
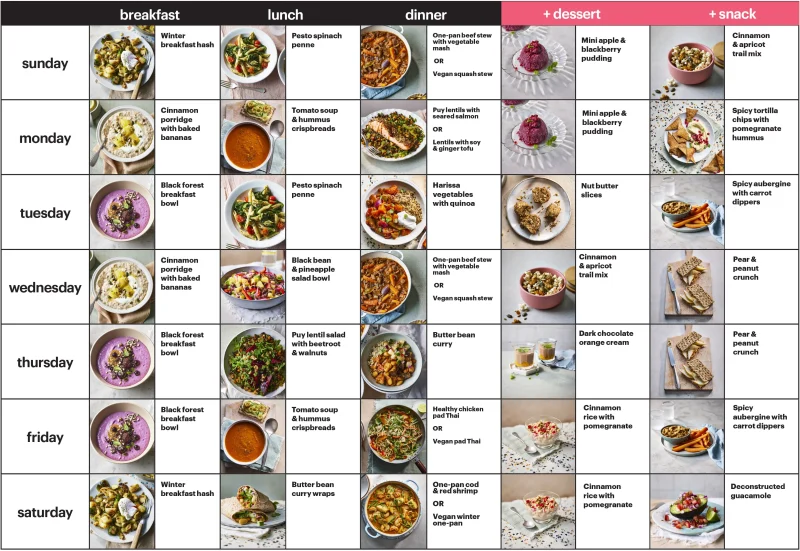
Sustainable nutrition is built on habits, not rules.
Helpful tips include:
-
Eating regular meals
-
Cooking more at home
-
Practicing mindful eating
-
Allowing flexibility for enjoyment
-
Focusing on progress, not perfection
Small, consistent actions lead to long-term health benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Do I need to follow a strict diet to eat balanced?
No. Balanced nutrition focuses on variety and moderation, not restriction.
2. Can balanced nutrition help with energy levels?
Yes. Balanced meals stabilize blood sugar and support consistent energy throughout the day.
3. Are supplements necessary for balanced nutrition?
Most people can meet their needs through food alone. Supplements should be used only when recommended by a healthcare professional.
4. How many meals should I eat per day?
There is no universal rule. What matters is meeting your nutrient needs consistently.
5. Is balanced nutrition expensive?
Not necessarily. Whole foods like grains, beans, fruits, and vegetables can be affordable and nutritious.
6. Can I enjoy treats and still eat balanced?
Yes. Balanced nutrition allows flexibility and enjoyment as part of a healthy lifestyle.
Conclusion
Understanding Balanced Nutrition Basics for Everyday Health provides a practical framework for nourishing your body without stress or confusion. By focusing on variety, moderation, and consistency, you can support your physical health, mental clarity, and long-term well-being.
Healthy eating is not about perfection—it’s about making better choices most of the time. Start small, stay consistent, and let balanced nutrition support a healthier, more energized life.





