How Daily Stress Affects Your Overall Health: 15 Alarming Effects You Shouldn’t Ignore

Stress has become an unavoidable part of modern life. Deadlines, financial pressure, digital overload, family responsibilities, and constant connectivity all contribute to ongoing tension. While short-term stress can sometimes be helpful, daily stress that remains unmanaged can silently damage the body and mind. Understanding How Daily Stress Affects Your Overall Health is essential for protecting your long-term well-being.
According to the World Health Organization, chronic stress is one of the leading contributors to non-communicable diseases worldwide. It doesn’t just affect how you feel emotionally—it impacts nearly every system in your body, from your heart and immune system to digestion, sleep, and mental clarity.
This in-depth guide explores the science-backed effects of daily stress, how it manifests in different areas of health, and what you can do to regain balance and resilience.
Understanding Stress and the Body
Stress is a natural biological response designed to protect us from danger. However, when stress becomes constant, it shifts from being helpful to harmful.
What Is Stress?
Stress is the body’s reaction to perceived threats or challenges. These threats can be physical, emotional, psychological, or environmental. When you experience stress, your body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, preparing you to respond.
Acute Stress vs. Chronic Stress
-
Acute stress is short-term and temporary, such as preparing for a presentation.
-
Chronic stress occurs when stressors persist over time without adequate recovery.
It’s chronic, daily stress that causes the most damage and explains How Daily Stress Affects Your Overall Health so profoundly.
How the Stress Response Works

The Fight-or-Flight Mechanism
When stress is triggered, the nervous system activates the “fight-or-flight” response. Heart rate increases, blood pressure rises, muscles tense, and digestion slows. This response is useful in emergencies—but harmful when activated continuously.
Over time, constant activation exhausts the body’s systems, leading to widespread health consequences.
Physical Health Effects of Daily Stress
Daily stress affects nearly every physical system in the body, often without obvious warning signs.
Cardiovascular Health
Chronic stress increases heart rate and blood pressure, placing constant strain on the cardiovascular system. Over time, this raises the risk of:
-
Hypertension
-
Heart disease
-
Stroke
Stress-related inflammation also contributes to plaque buildup in arteries, making heart health one of the most serious areas impacted by daily stress.
Immune System Suppression
High cortisol levels suppress immune function. This means people under chronic stress are more likely to:
-
Catch colds and infections
-
Experience slower wound healing
-
Have increased inflammation
Understanding How Daily Stress Affects Your Overall Health helps explain why stress often leads to frequent illness.
Digestive Problems
The gut and brain are closely connected. Chronic stress disrupts digestion and gut bacteria balance, leading to:
-
Acid reflux
-
Irritable bowel symptoms
-
Bloating and nausea
-
Appetite changes
Stress can either suppress hunger or lead to emotional eating, both of which harm digestive health.
Hormonal Imbalances
Long-term stress interferes with hormonal regulation. Elevated cortisol disrupts:
-
Insulin balance
-
Thyroid function
-
Reproductive hormones
This can result in weight gain, fatigue, irregular menstrual cycles, and reduced libido.
Sleep Disruption
Stress and sleep have a bidirectional relationship. Stress makes it difficult to fall or stay asleep, while lack of sleep increases stress sensitivity.
Poor sleep leads to:
-
Reduced cognitive performance
-
Lower emotional regulation
-
Increased risk of chronic illness
Sleep deprivation is one of the clearest examples of How Daily Stress Affects Your Overall Health.
Mental and Emotional Health Impacts
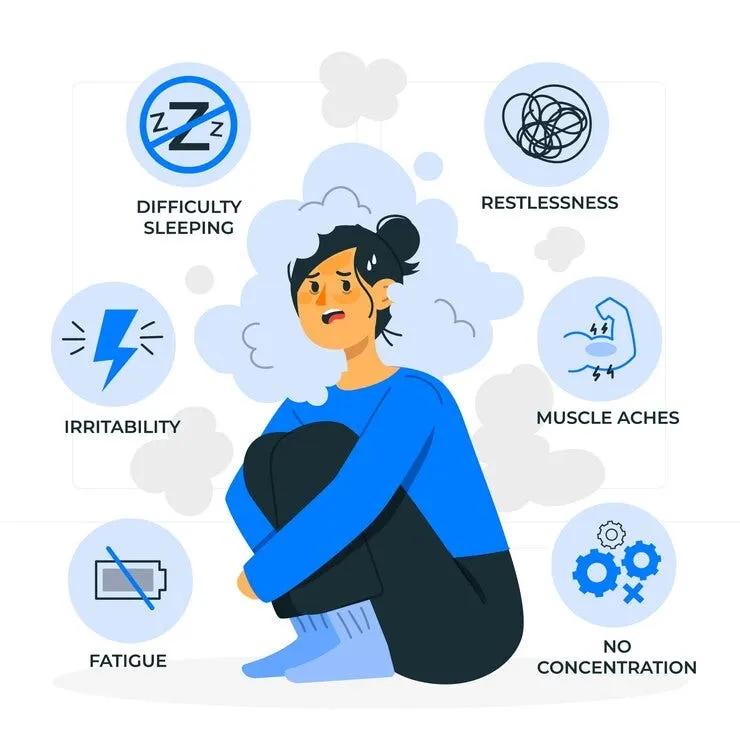
The psychological effects of stress are often the most noticeable—and the most distressing.
Anxiety and Depression
Chronic stress alters brain chemistry and increases vulnerability to anxiety and depressive disorders. Persistent worry, irritability, and feelings of hopelessness often stem from prolonged stress exposure.
Cognitive Decline and Focus Issues
Stress affects memory, attention, and decision-making. High cortisol levels damage the hippocampus, the brain region responsible for learning and memory.
Common symptoms include:
-
Brain fog
-
Poor concentration
-
Forgetfulness
-
Reduced problem-solving ability
Emotional Exhaustion and Burnout
Burnout occurs when emotional and mental resources are depleted. It often presents as:
-
Detachment
-
Low motivation
-
Cynicism
-
Feeling overwhelmed
Burnout is a clear warning sign that daily stress has exceeded the body’s coping capacity.
Behavioral and Lifestyle Consequences

Unhealthy Coping Habits
When stress is unmanaged, people often turn to unhealthy behaviors such as:
-
Overeating or undereating
-
Smoking or excessive alcohol use
-
Excessive screen time
-
Social withdrawal
These habits worsen physical and mental health, creating a harmful cycle.
Reduced Physical Activity
Stress drains energy and motivation, making regular exercise feel overwhelming. Reduced movement further increases stress levels, muscle tension, and cardiovascular risk.
Long-Term Health Risks of Chronic Stress
Increased Risk of Chronic Disease
Over time, chronic stress significantly increases the risk of:
-
Heart disease
-
Type 2 diabetes
-
Autoimmune disorders
-
Obesity
-
Mental health disorders
Understanding How Daily Stress Affects Your Overall Health is crucial for preventing these long-term conditions rather than treating them later.
Effective Ways to Manage Daily Stress
Managing stress does not require eliminating stressors entirely—only learning how to respond differently.
Lifestyle and Mindset Strategies
Proven stress-management techniques include:
-
Regular physical activity
-
Deep breathing and mindfulness meditation
-
Setting healthy boundaries
-
Prioritizing sleep and nutrition
-
Taking breaks from digital devices
-
Practicing gratitude and self-compassion
Even small changes practiced consistently can reverse many harmful stress effects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can daily stress really cause physical illness?
Yes. Chronic stress contributes to inflammation, immune suppression, and hormonal imbalance, all of which increase disease risk.
2. How much stress is considered unhealthy?
Stress becomes unhealthy when it is persistent, overwhelming, and interferes with sleep, mood, or daily functioning.
3. Can stress affect weight?
Yes. Stress alters appetite-regulating hormones and often leads to weight gain or loss.
4. Is stress ever beneficial?
Short-term stress can improve focus and performance. Long-term stress is harmful.
5. How quickly can stress management improve health?
Some improvements, like better sleep and mood, can appear within weeks of consistent stress management.
6. Should I seek professional help for stress?
If stress feels unmanageable or leads to anxiety, depression, or physical symptoms, professional support is strongly recommended.
Conclusion
Understanding How Daily Stress Affects Your Overall Health is the first step toward reclaiming control over your well-being. While stress is unavoidable, its harmful effects are not inevitable. By recognizing the signs early and adopting healthy coping strategies, you can protect your body, strengthen your mind, and improve your quality of life.
Stress does not have to define your health. Small, consistent actions can restore balance and resilience over time.





